New Patients
(860) 218-9463
Existing Patients
(860) 421-0144
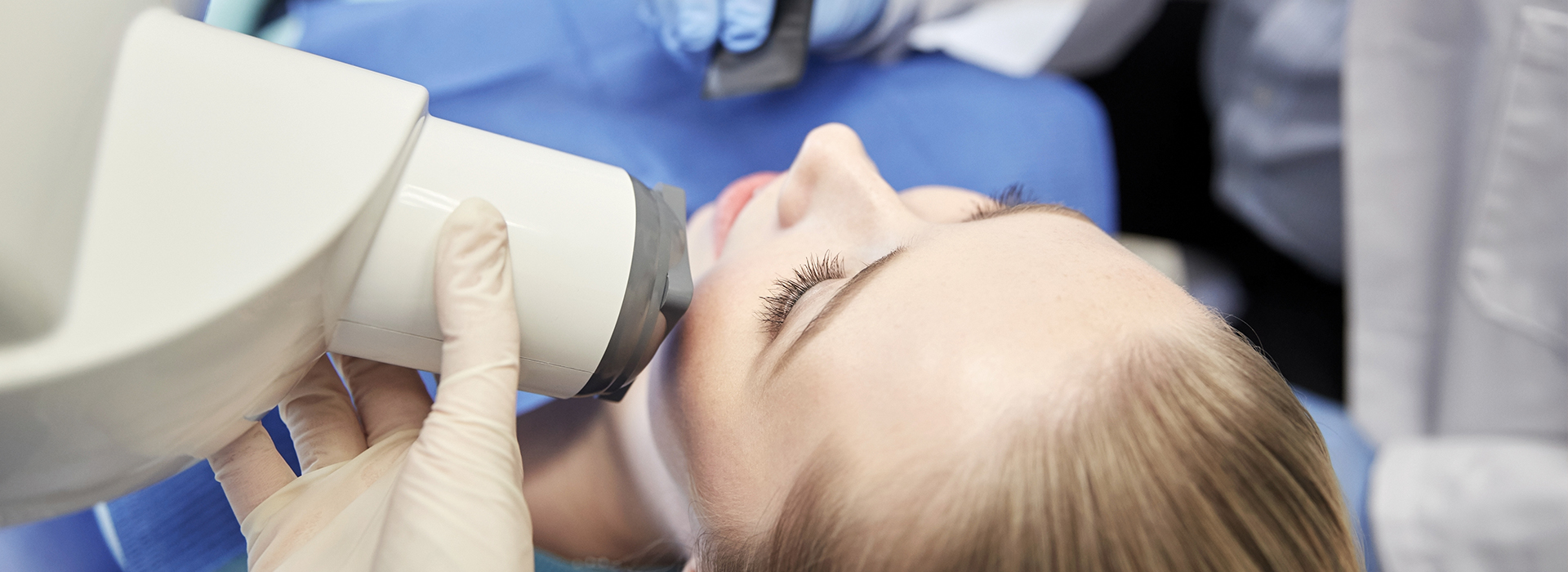
Digital radiography is the modern method of capturing dental X-ray images using electronic sensors and computer systems instead of traditional photographic film. This approach converts X-ray exposure into digital files that can be viewed immediately on a monitor, making the process faster and more convenient for both patients and clinicians. At its core, digital radiography streamlines how images are acquired, examined, and stored while preserving the diagnostic value that dentists rely on to see what is happening beneath the surface of the teeth and gums.
Beyond convenience, digital radiography changes how care is delivered: clinicians can magnify images, adjust contrast, and annotate findings without degrading the image itself. Those capabilities help dentists evaluate conditions such as cavities, root structure, bone levels, and the fit of restorations with greater clarity. The result is a more efficient diagnostic workflow that supports informed treatment planning and clearer communication with patients.
Because dental X-rays are a routine part of preventative and restorative care, using a modern imaging system affects the patient experience every time X-rays are taken. Patients get results faster, clinicians have more tools for interpretation, and the practice can keep more organized, accessible records. For anyone curious about how imaging influences treatment decisions, digital radiography is a practical technology worth understanding.
Instead of putting film into the mouth, digital radiography uses small sensors positioned where the film used to go. When the X-ray exposure occurs, the sensor converts the radiation into an electronic signal that is instantly processed by software and saved to the patient’s digital chart. Some systems create the image directly from the sensor, while others capture a phosphor plate that is scanned, but both approaches eliminate the need for chemical developers and physical darkrooms.
The digital workflow is straightforward: position, expose, and review. The clinician or assistant places a sensor inside the patient’s mouth, aligns the X-ray source, and triggers a short exposure. Within seconds the image appears on a computer screen where it can be inspected, enhanced, and compared with previous images. This immediacy reduces the chance of retakes caused by improper placement or movement because adjustments can be made right away.
Sensor technology and software have improved steadily, resulting in higher resolution images at lower doses of radiation. The sensors themselves are designed with patient comfort in mind, featuring slim profiles and rounded edges to minimize gag reflex and discomfort. Taken together, these technical improvements make the entire imaging experience quicker, gentler, and more informative than earlier film-based methods.
One of the most visible benefits of digital radiography is speed. Patients no longer wait through a chemical development process to see images; instead, they and the dental team can review X-rays together immediately after they are taken. This helps patients better understand diagnoses and proposed treatments because clinicians can point to specific areas on the image, adjust brightness or contrast, and use on-screen tools to highlight concerns.
Safety and dose reduction are also central advantages. Because digital sensors are more sensitive to X-ray energy than traditional film, acceptable diagnostic images usually require lower radiation exposure. Clinicians still follow standard radiation safety protocols, but the efficiency of sensors makes routine imaging safer when compared to older approaches. That combination of reduced exposure and faster processing creates a more reassuring imaging experience for patients.
Image clarity and flexibility further improve diagnostic accuracy. Digital images can be enhanced—magnified, sharpened, or color-adjusted—without losing detail, which helps detect subtle changes such as early decay or small fractures. The ability to compare current and past images side-by-side also supports long-term monitoring of oral health, enabling more timely interventions when changes occur.
In our practice, digital radiography is integrated into routine exams, treatment planning, and follow-up care. During a comprehensive checkup, targeted X-rays help the dental team examine areas that aren’t visible during a clinical exam alone—between teeth, below restorations, and beneath the gumline. For planned procedures, such as root canals or implant evaluations, digital images provide essential information that guides precise, evidence-based decisions.
When discussing treatment options, clinicians use on-screen images to explain findings and illustrate recommended next steps. This visual approach empowers patients to make informed choices by seeing the same images the dental team is using to assess their condition. The result is clearer communication and a collaborative process where questions can be answered using the actual diagnostic material.
Newpoint Family Dental employs digital imaging as a routine part of care because it supports safer, faster, and more accurate diagnoses. Our team uses industry-standard software and sensor technology to ensure images are captured and interpreted consistently, and we focus on making the imaging portion of every visit as comfortable and efficient as possible for patients of all ages.
Once an image is captured, it becomes a digital asset tied to the patient’s chart. This makes organization and retrieval simple: images can be archived, indexed by date, and compared with prior films to track changes over time. Digital storage also reduces the risk of lost or damaged files and frees the office from maintaining physical film archives that require space and special handling.
Digital images are also easy to share securely with other clinicians when collaborative care is needed. Whether coordinating with a specialist or transmitting records for a referral, the digital format enables prompt, high-quality image transfer without mailing physical film. This improves continuity of care and allows outside providers to make efficient assessments based on the same visual information the practice used in planning treatment.
From an administrative standpoint, digital imaging supports efficient recordkeeping and compliance with data-protection practices. Images remain part of a comprehensive electronic record that helps the team deliver consistent, well-documented care. For patients, that means the information used to guide their dental treatment is reliable, accessible, and managed with attention to confidentiality and clinical quality.
In summary: digital radiography modernizes dental imaging by combining faster acquisition, improved image quality, and streamlined recordkeeping. It enhances diagnostic confidence, supports clearer communication between clinicians and patients, and reduces the environmental footprint associated with film processing. If you’d like to learn more about how digital X-rays are used during exams and procedures or have questions about what to expect at your next visit, please contact us for more information.
